What are J-Credits? Unlocking the Key Points for Your Decarbonization
The world is buzzing about decarbonization, and for good reason. Companies everywhere are looking for ways to reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. If you’re tackling this challenge, you’ve likely heard the term “J-Credits.” But what exactly are they, and how can they become a powerful tool in your company’s sustainability journey?
J-Credits are a system that certifies and allows for the trading of greenhouse gas emission reductions and absorption amounts as “credits.” By utilizing J-Credits, companies can advance their decarbonization initiatives more easily and gain various other benefits. As corporate environmental conservation efforts become increasingly important, understanding the fundamentals of J-Credits is essential.
This article will introduce the essential points for effectively leveraging J-Credits in your organization’s decarbonization efforts, including an overview, benefits, and considerations. If you are a company representative currently engaged in or planning to embark on decarbonization, we hope this article will be a useful reference for you.

目次
What are J-Credits?
J-Credits are a system that allows for the trading of environmental value contributed through CO2 emission reductions. Besides J-Credits, other forms of environmental value include Non-Fossil Certificates and Green Electricity Certificates. Let’s explore the mechanism of J-Credits and the background behind the carbon credit system.
The J-Credit Mechanism
The J-Credit system certifies and allows for the trading of greenhouse gas emission reductions and absorption amounts as “credits.” Companies and local governments that contribute to greenhouse gas emission reductions by introducing energy-saving equipment or renewable energy, or by increasing absorption through forest conservation and afforestation, can sell the environmental value they’ve contributed as “credits.”
Conversely, companies aiming to achieve decarbonization goals, such as CO2 emission reduction, can indirectly contribute to greenhouse gas emission reductions by purchasing J-Credits. By enabling the trading of environmental value, the J-Credit mechanism further promotes investment in equipment and initiatives for decarbonization.

J-Credits vs. Non-Fossil Certificates vs. Green Electricity Certificates
Environmental value comes in various forms, including J-Credits, Non-Fossil Certificates, and Green Electricity Certificates. Understanding the characteristics of each is crucial for choosing the best option for your specific objectives.
| J-Credits vs. Non-Fossil Certificates vs. Green Electricity Certificates | |
| J-Credits |
|
| Non-Fossil Certificates |
|
| Green Electricity Certificates |
|
Generally, any of these environmental certificates can be used for reporting purposes under the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures. However, for RE100 reporting, there may be specific conditions as outlined above. Therefore, it’s vital to choose the environmental certificate that best suits your intended use.
Why Carbon Credits Are Gaining Traction
To forge a carbon-neutral society and fulfill the Paris Agreement, carbon credit systems like J-Credits are gaining significant traction.
【What is the Paris Agreement?】
|
This enables companies, even those finding it difficult to directly invest in carbon reduction efforts like installing energy-efficient equipment or adopting renewable energy, to actively contribute to a low-carbon future.
This will also lead to a positive cycle where increased demand for electricity derived from renewable energy sources will, in turn, encourage greater generation of renewable energy.
J-Credits: A Growing Trend
Originally, J-Credits were set to operate temporarily until fiscal year 2030, but the system’s continuation beyond 2030 has now been confirmed. With the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and the Ministry of the Environment (MOE) at the forefront, various initiatives are being implemented across demand, supply, and distribution to further promote the use of environmental certificates. This proactive approach suggests that J-Credits are poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
For example, here are some key policies designed to boost the demand for J-Credits:
・Revised Energy Conservation Act creates new avenues for use
・J-Credit Joins CORSIA
・Revised Act on Promoting Green Procurement incorporates offsetting etc.
※Reference: METI 経済産業省「カーボンクレジット・レポートを踏まえた政策動向」 (Japanese)
Revised Energy Conservation Act Creates New Avenues for Use:
The revised Energy Conservation Act, enacted in 2022, now requires specified businesses to submit medium-to-long-term plans and regular reports on their progress toward converting to non-fossil energy sources (including non-fossil fuels and heat/electricity generated from non-fossil sources). By utilizing J-Credits derived from non-fossil heat and electricity, businesses can be considered to have expanded their use of non-fossil energy, which is expected to drive demand.
J-Credit Joins CORSIA:
CORSIA (Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation) is a mechanism by the International Civil Aviation Organization to curb CO2 emissions from international flights. J-Credits’ participation in CORSIA allows them to be used for offsetting emissions in the aviation industry, which has substantial reduction obligations, potentially amounting to millions of tons annually. This opens up a significant new demand avenue for J-Credits.
Revised Act on Promoting Green Procurement Incorporates Offsetting:
The Act on Promoting Green Procurement promotes the selection of environmentally friendly products by government agencies and local authorities when making purchases. A recent revision to this act now includes carbon offsetting as a consideration for certain eligible items. This is anticipated to increase demand for J-Credits as carbon offsetting using them becomes more widespread.
Behind these initiatives to expand J-Credit demand lies the fact that the quality of FIT Non-Fossil Certificates, another type of environmental certificate, has improved, and their prices have been lowered.
Given these circumstances, the reality is that J-Credits’ relative competitiveness has declined. To address this, policies aimed at increasing demand are being implemented. It is crucial to understand this background when considering the extent to which J-Credits should be incorporated into your efforts.
J-Credits: Benefits and Considerations
The J-Credit scheme offers advantages for both purchasing and selling companies. However, there are also points to be aware of. Let’s explore some key examples to ensure you can utilize J-Credits effectively.
| J-Credits: Benefits & Considerations | |
| Benefits | 【For Purchasing Companies: 】 ・Enhances corporate image ・Stronger branding 【For Selling Companies: 】 ・Generates sales profits ・Enhances corporate image ・Leads to new network building |
| Considerations | ・Complex registration procedures for credits ・Takes time to receive sales profits |
Let’s delve a bit deeper into each of these points
Benefits of J-Credits
By purchasing J-Credits, you can indirectly contribute to CO2 emission reductions through the introduction of energy-saving equipment, renewable energy, and proper forest management.
Furthermore, J-Credits can be utilized for reporting under regulations such as the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures and the Energy Conservation Act. This can elevate your company’s reputation as a leader in decarbonization initiatives, leading to stronger branding and an improved corporate image.
Compared to other environmental certificates, a key strength of J-Credits is that they have no expiration date. This offers flexibility; even if you can’t use all purchased credits within a single fiscal year, they can be carried over for offsetting in subsequent years.
On the other hand, for companies that generate and sell J-Credits, there are significant advantages. These include showcasing their decarbonization efforts through the adoption of energy-saving equipment and renewable energy, which boosts their corporate image. Moreover, the profits from selling J-Credits can help offset a portion of their equipment investment costs, potentially encouraging further environmental investments.
Additionally, by trading J-Credits—for instance, when credits generated are utilized by local businesses or public organizations—new networks can be built, and new business opportunities may emerge.

Considerations for J-Credits
It’s important to note that the registration procedures for obtaining sales profits from J-Credits can be complex, and it may take time to receive those profits.
This is because J-Credit certification requires going through procedures such as project approval and auditing. Furthermore, even after certification, sales profits are not realized until transactions are finalized. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider that it will take a certain amount of time when planning your utilization strategy.
Another key point to consider moving forward is the impact of the improved quality and reduced price of FIT Non-Fossil Certificates. As the relative competitiveness of J-Credits declines, it will be necessary to also consider selecting other environmental certificates.
Understanding J-Credit Trading Prices
One of the most common questions when considering J-Credits likely revolves around their trading price. Let’s explore the overview and current trends in J-Credit pricing.
J-Credit Trading Prices Fluctuate
J-Credits are bought and sold through two primary methods: over-the-counter (OTC) transactions and auction sales. This means there’s no fixed price for J-Credits; their trading value fluctuates depending on the market conditions of these transactions and auctions.
OTC transactions for J-Credits can be conducted in any of the following ways:
- Directly trading with the credit holder
- Utilizing an intermediary
- Using the J-Credit Scheme website
The list of available credits published on the J-Credit Scheme website allows you to search for purchasable credits based on quantity and characteristics (e.g., location, region, specific activity details).
If a trade has not been finalized for more than six months after being listed on the J-Credit Scheme website, the credits become eligible for auction. Auctions are typically held approximately twice a year by the J-Credit Scheme Secretariat.
J-Credit Trading Prices Are on an Upward Trend
J-Credit trading prices are currently on an upward trend. This is due to the rising demand for environmental certificates and renewable energy in recent years, driven by government policies promoting carbon neutrality.
According to the latest data from the J-Credit Scheme Secretariat, the average trading price in the 13th auction in April 2022 reached a record high for both renewable energy generation and energy conservation credits.
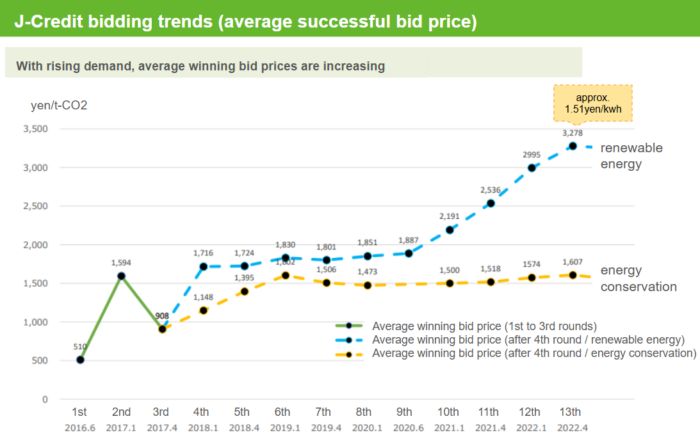
Note: translated by Shizen Energy based on source from the J-Credit Scheme Administrator
J-クレジット制度について(データ集)(J-クレジット制度事務局) (Japanese)
As companies are increasingly required to promote initiatives for CO2 emission reduction to achieve a decarbonized society, the demand for environmental certificates is expected to remain high. However, it’s important to note that J-Credit trading prices could potentially decrease due to their relationship with the prices of other environmental certificates.
Shizen Energy Inc. offers services to support the purchase of credits such as J-Credits and Non-Fossil Certificates. If you wish to learn more about the types of credits and implementation methods for more concrete decarbonization efforts, please refer to the page below.
Summary
J-Credits are a type of environmental value, a system that certifies and allows for the trading of greenhouse gas emission reductions and absorption amounts as “credits.” They are an effective option for incorporating partial carbon offsets into your CO2 reduction efforts to achieve even greater results. We hope the points introduced in this article will help you leverage J-Credits and other environmental values in your company’s decarbonization journey.





